Rho
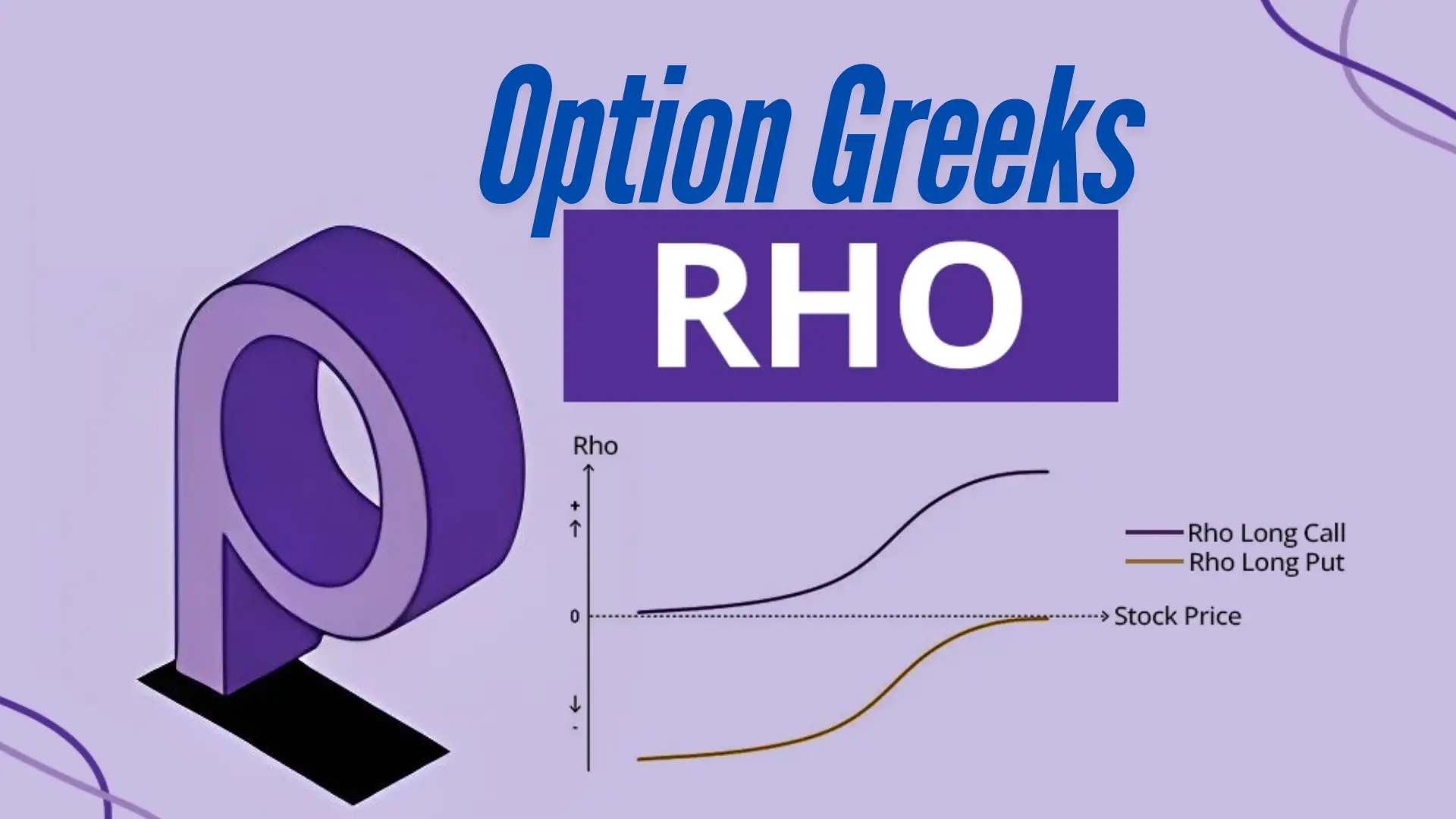
Rho is the part of option Greek that measures how sensitive an option's price is to changes in interest rates. In simpler terms, it tells us how much the price of an option might change if interest rates go up or down.
It's worth noting that rho tends to have a smaller impact on option prices compared to some of the other Greeks, especially for options with shorter expiration dates. Rho can be important, especially for long-term options.
How to work Rho?
Here's how rho typically behaves:
For call options, rho is usually positive. This means that as interest rates increase, the value of the call option tends to increase as well.
For put options, rho is usually negative. So, when interest rates go up, the value of the put option tends to decrease.
Why does this happen? Well, it's related to the concept of the time value of money. When interest rates are higher, the present value of the option's exercise price becomes lower, which is good for call options but not so great for put options.
How to Calculate Rho?
Now, I won't bore you with complex formulas, but it's good to know that rho is typically expressed as the expected change in the option's price for a 1% change in interest rates. For example, if a call option has a rho of 0.05, its price would be expected to increase by ₹0.05 if interest rates increased by 1%.
What factors will affect Rho?
Several factors can influence rho:
Time to expiration: Longer-term options are more sensitive to interest rate changes, so they tend to have higher rho values.
Option type: As mentioned earlier, call options usually have positive rho, while put options usually have negative rho.
How far the option is in-the-money or out-of-the-money: At-the-money options tend to have the highest rho values.