📌 Table of Contents
- Introduction to SME IPO
- Overall SME IPO Timeline Overview
- Phase 1: Pre-IPO Preparation
- Phase 2: Drafting & Filing Offer Document
- Phase 3: Roadshows and Marketing
- Phase 4: The Public Issue
- Phase 5: Post-Issue Activities and Listing
- Phase 6: Post-Listing Compliance
- SME IPO Step-by-Step Process
- Conclusion
Introduction to SME IPO
An SME IPO (Initial Public Offering) is a mechanism that allows small and medium enterprises to raise funds by offering shares to the public and becoming listed entities. Unlike mainboard IPOs, SME IPOs are tailored to the unique needs of growing businesses and come with relaxed eligibility norms.
The goal is to enhance access to capital markets and fuel expansion while adhering to a simplified regulatory framework.
Overall SME IPO Timeline Overview
The process of an SME IPO is structured across six main phases and typically takes about 4 to 6 months to complete. Here’s a breakdown:
| Phase | Key Activities | Indicative Timeline | Key Participants |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-IPO Preparation | Strategy, due diligence, restructuring | 4–8 Weeks | Company, Merchant Banker, Legal Team |
| Offer Document Preparation | Drafting & filing DRHP/Prospectus | 6–10 Weeks | Merchant Banker, Auditors, NSE/BSE |
| Marketing & Roadshows | Investor outreach, pricing | 2–3 Weeks | Company, Merchant Banker |
| Public Issue | Collecting applications via ASBA | 1 Week | Investors, Registrars, Banks |
| Post-Issue & Listing | Allotment, Demat credit, listing | 2–3 Weeks | Stock Exchange, Depositories |
| Post-Listing Compliances | SEBI filings, disclosures, governance | Ongoing | Company Secretary, Market Maker |
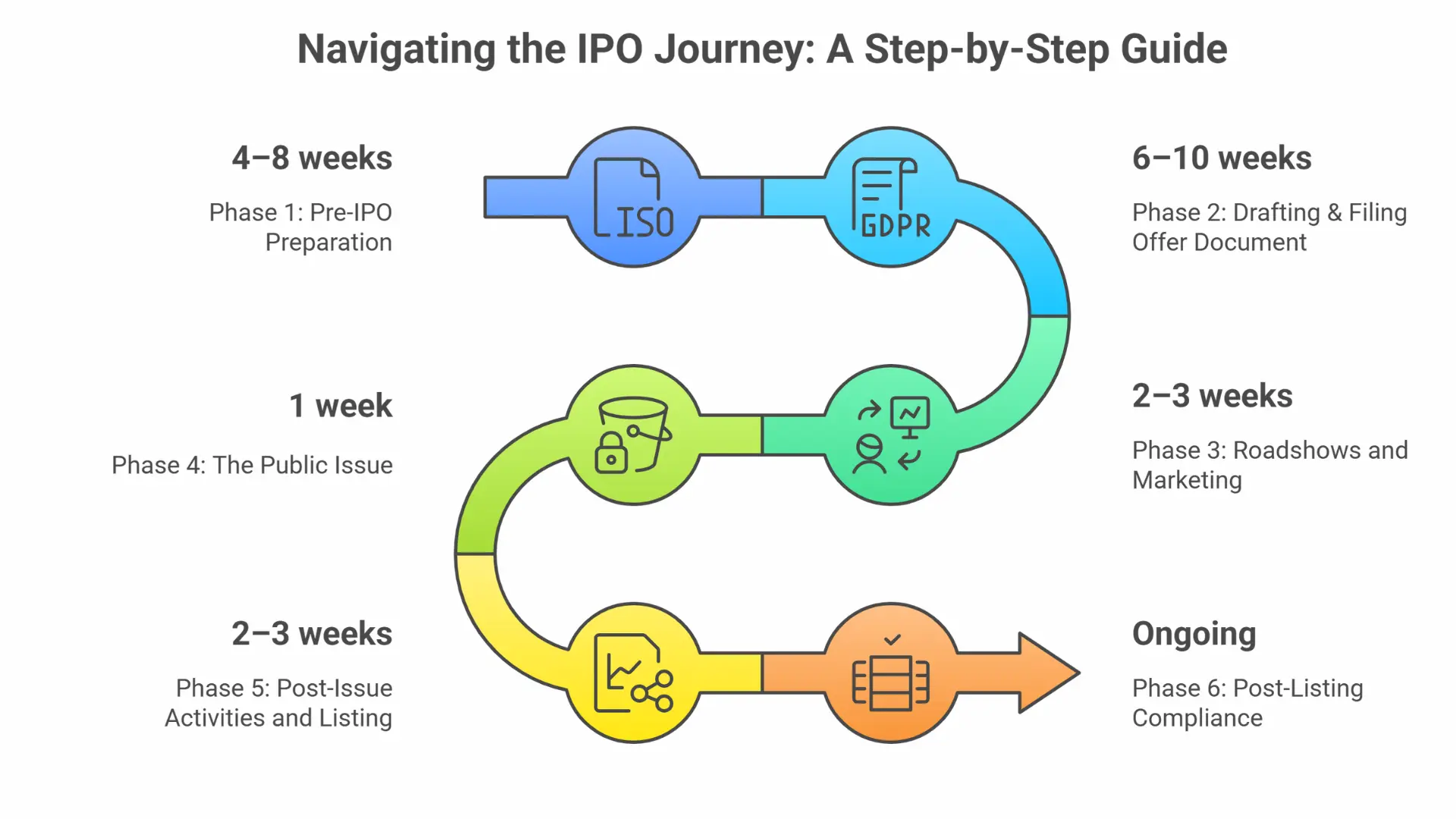
Phase 1: Pre-IPO Preparation
This is the foundation phase where the company aligns its internal processes and team for the IPO journey.
Key Activities:
- Assess IPO objectives and financial needs.
- Appoint a Merchant Banker and other intermediaries such as legal counsel, registrar, auditors, and market makers.
- Conduct due diligence on legal, financial, and operational fronts.
- Restructure corporate and capital frameworks if needed.
- Determine the issue type (fixed price or book building) and size.
Typical Duration: 4–8 weeks
Phase 2: Drafting & Filing Offer Document
Once the groundwork is done, the company collaborates with its advisors to prepare the Draft Red Herring Prospectus (DRHP) or Prospectus.
Key Activities:
- Prepare DRHP with detailed company info, risk factors, financial data, and business strategy.
- File DRHP with the stock exchange (NSE Emerge or BSE SME).
- Receive in-principle approval after review and due diligence by the exchange.
- Appoint a market maker (mandatory for SME IPOs).
Typical Duration: 6–10 weeks
Phase 3: Roadshows and Marketing
Marketing is a crucial phase where the company and merchant banker engage investors and raise awareness about the IPO.
Key Activities:
- Conduct roadshows and presentations to attract interest from retail, HNI, and institutional investors.
- Decide and announce the issue price or price band.
- File the final RHP (Red Herring Prospectus) with the Registrar of Companies (ROC) and the stock exchange.
Typical Duration: 2–3 weeks
Phase 4: The Public Issue
The IPO is now open to the public for subscription, and applications are collected via ASBA (Application Supported by Blocked Amount).
Key Activities:
- Open the IPO window for 3 to 10 working days.
- Collect investor bids and funds.
- Track real-time subscription levels by category (retail, HNI, etc.).
Typical Duration: 1 week
Phase 5: Post-Issue Activities and Listing
Once the public issue is closed, post-issue formalities are completed before listing.
Key Activities:
- Finalize the basis of allotment.
- Refund unsuccessful applicants.
- Credit allotted shares to investors' Demat accounts.
- Obtain listing approvals.
- Shares commence trading on NSE Emerge or BSE SME.
Typical Duration: 2–3 weeks
Phase 6: Post-Listing Compliance
After the listing, the company must adhere to ongoing regulatory and disclosure norms set by SEBI.
Key Activities:
- Market maker ensures liquidity for at least 3 years.
- Submit quarterly and half-yearly financials, shareholding patterns, and corporate governance reports.
- Maintain effective investor communication and transparency.
Duration: Ongoing
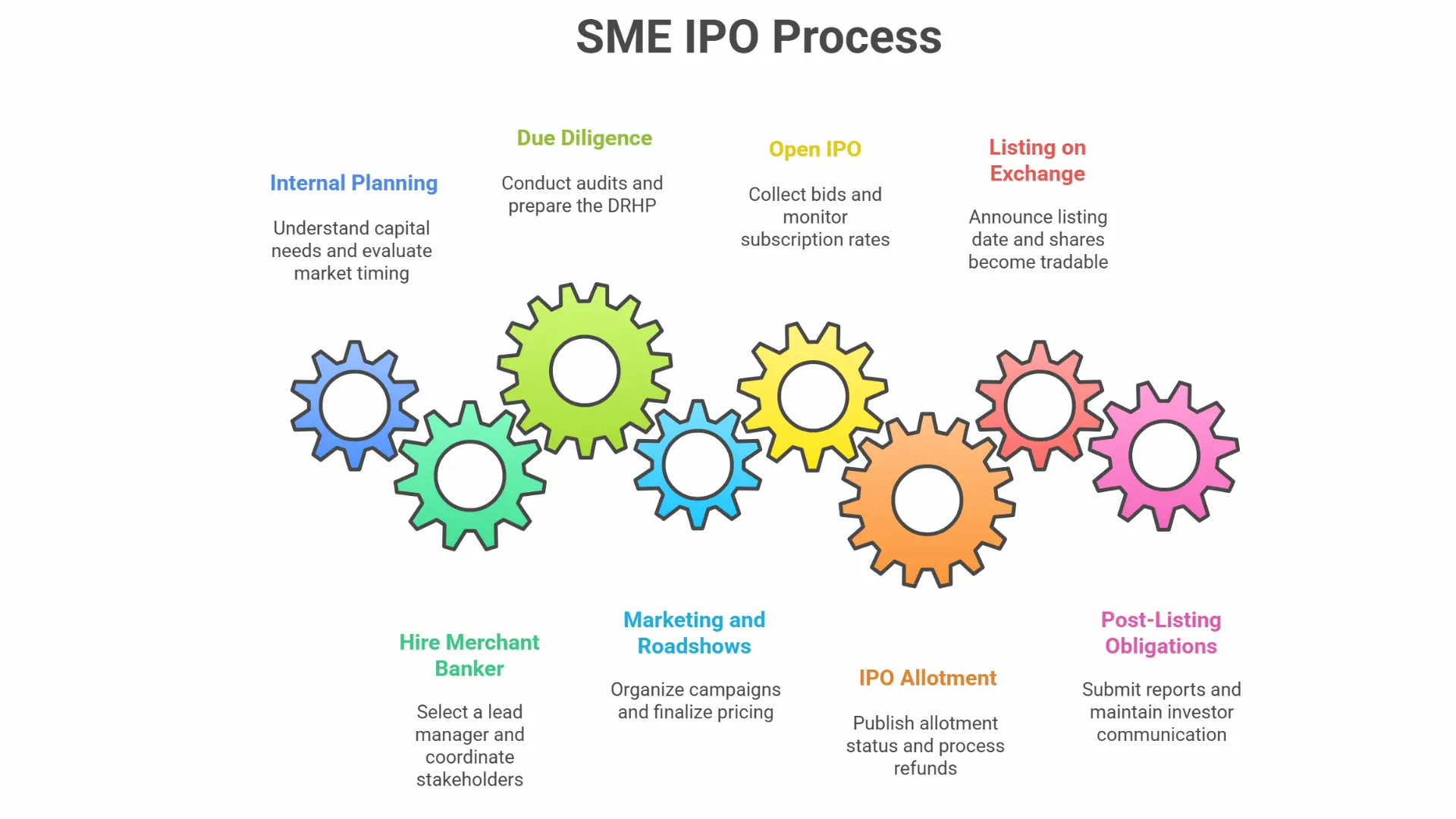
SME IPO Step-by-Step Process
Here’s a consolidated, easy-to-follow checklist for an SME IPO:
1. Internal Planning
- Understand capital needs.
- Evaluate market timing.
- Conduct board meetings and pass necessary resolutions.
2. Hire a SEBI-registered merchant Banker
- Select a merchant banker to act as lead manager.
- Coordinate with other stakeholders (auditors, registrars, market makers).
3. Due Diligence and Offer Document Preparation
- Financial, legal, and business audits.
- Prepare and file the DRHP.
- Obtain exchange approval and ROC clearance.
4. Marketing and Investor Roadshows
- Organize awareness campaigns.
- Finalize the price band or issue price.
5. Open the IPO to the Public
- Collect bids via ASBA.
- Monitor subscription rates.
6. IPO Allotment
- Registrar publishes the allotment status.
- Refunds and Demat credit processed.
7. Listing on the Stock Exchange
- Exchange announces listing date and price.
- Shares become tradable with an assigned ISIN or scrip code.
8. Post-Listing Obligations
- Submit financials, governance reports, and other mandatory filings.
- Continue market making and investor communication.
Conclusion
Launching an SME IPO in India is a transformative journey that unlocks capital, strengthens governance, and enhances brand equity. While the timeline may seem intensive, a well-prepared company with the right advisors can navigate the process smoothly within 4–6 months.
Whether you're an SME founder, investor, or stakeholder, understanding each phase of the SME IPO process equips you to make informed decisions and achieve long-term success on the stock market.

