Table of Contents
🔍What is a Long Put Option Strategy?
A Long Put Option Strategy is a simple options trading strategy that profits when the underlying asset’s price falls. It involves buying a Put Option, giving the trader the right (but not the obligation) to sell the asset at a specific price (strike price) before the expiry.
This strategy is ideal for traders with a bearish outlook on the market who want to benefit from a price decline, with limited downside risk.
Here's the Long Put Option Payoff Graph, which shows the profit and loss (P&L) at expiry for a long put position:
📈 Long Put Payoff Graph Details
- X-axis: Stock Price at Expiry (₹)
- Y-axis: Net Payoff (₹)
- Breakeven Point = Strike Price − Premium Paid
- Maximum Profit = Strike Price − Premium (when stock price drops to zero)
- Maximum Loss = Premium Paid (if the stock price ends above strike)
✅ Example Assumptions
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Strike Price | ₹500 |
| Premium Paid | ₹20 |
| Breakeven | ₹480 |
| Lot Size | 1 (for simplicity) |
🧮 Payoff Table
| Stock Price at Expiry (₹) | Intrinsic Value | Net Payoff = (Strike − Price − Premium) |
|---|---|---|
| 550 | 0 | -20 |
| 520 | 0 | -20 |
| 500 | 0 | -20 |
| 480 | 20 | 0 |
| 450 | 50 | +30 |
| 400 | 100 | +80 |
| 350 | 150 | +130 |
| 300 | 200 | +180 |
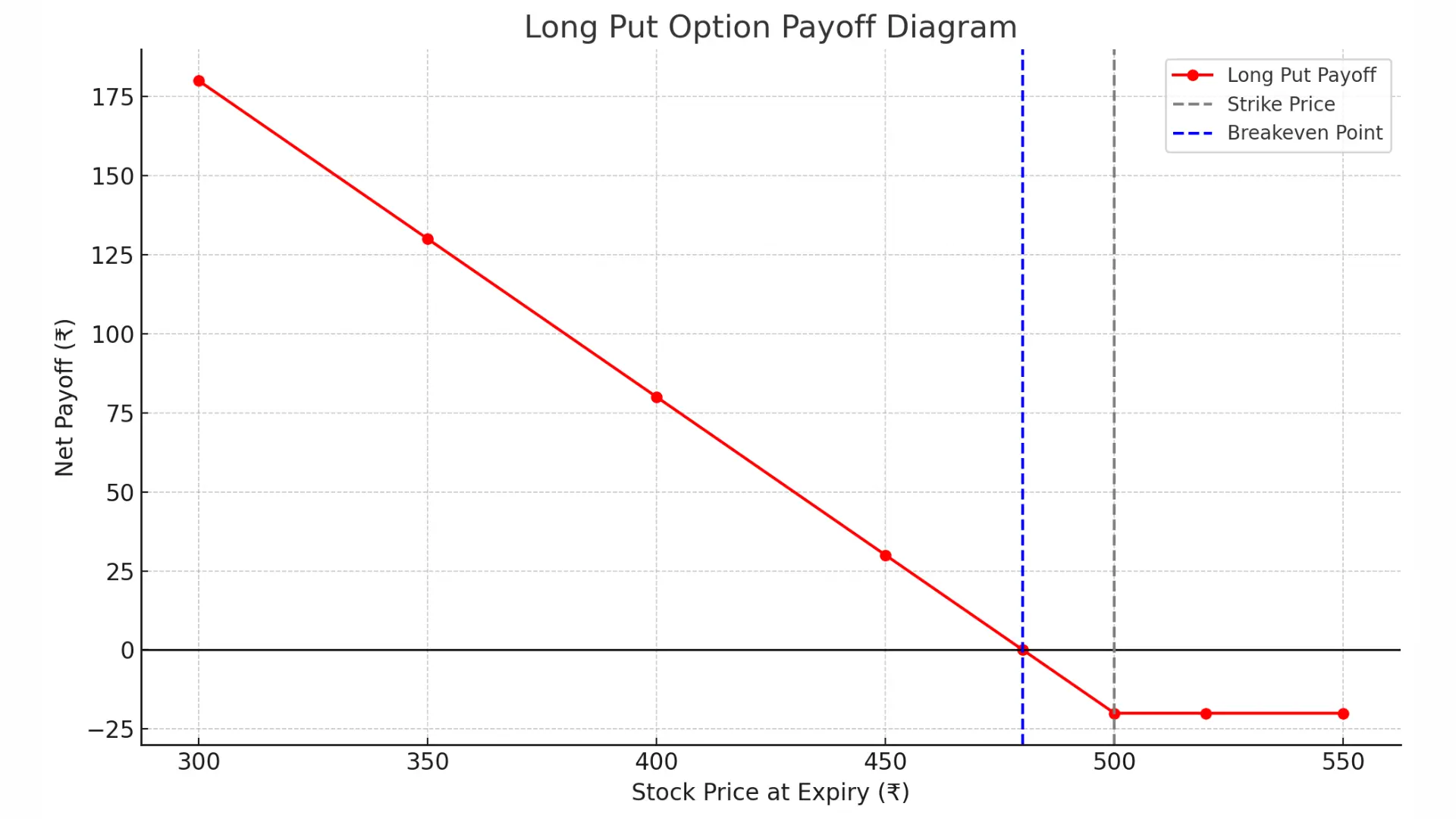
📊 Long Put Payoff Chart
I'll now generate a graph based on this data.
Here is the Long Put Option Payoff Graph:
- 🔴 Red Line: Net payoff for holding a long put.
- ⚫ X-axis: Stock Price at Expiry.
- 🔹 Blue dashed line: Breakeven point (₹480).
- ⚪ Gray dashed line: Strike price (₹500).
As seen:
- If the stock falls below ₹480, you start making a profit.
- If it stays above ₹500, your loss is limited to the premium paid (₹20).
- The lower the stock price, the higher the profit (up to the strike minus premium).
🧠Key Features
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Instruments Used | Put Options |
| Market Outlook | Bearish |
| Risk | Limited to premium paid |
| Reward | Theoretically unlimited |
| Breakeven Point | Strike Price – Premium Paid |
📊Why Use a Long Put Strategy?
The Long Put strategy allows traders to:
- Capitalize on falling prices.
- Take a bearish position with limited capital.
- Limit losses to just the premium paid.
- Avoid the unlimited risk involved in short-selling stocks.
Unlike holding a short position in equities, a long put comes with a clear, predefined risk, making it a smart alternative for risk-conscious traders.
📌When to Use Long Put Strategy
Use the Long Put strategy when:
- You expect the underlying asset to decline sharply.
- Market volatility is rising.
- You want to limit your loss to the premium.
🛠️How to Execute a Long Put Strategy
Let’s say NIFTY is currently trading at ₹25,000. You believe it will fall.
Example Setup:
| Action | Contract | Strike Price | Premium |
| Buy 1 Put | NIFTY 25JUL 25,000 PE | ₹25,000 | ₹150 |
If NIFTY falls, your Put option gains value. If NIFTY rises, the maximum you lose is the premium.
📘Real-World Examples
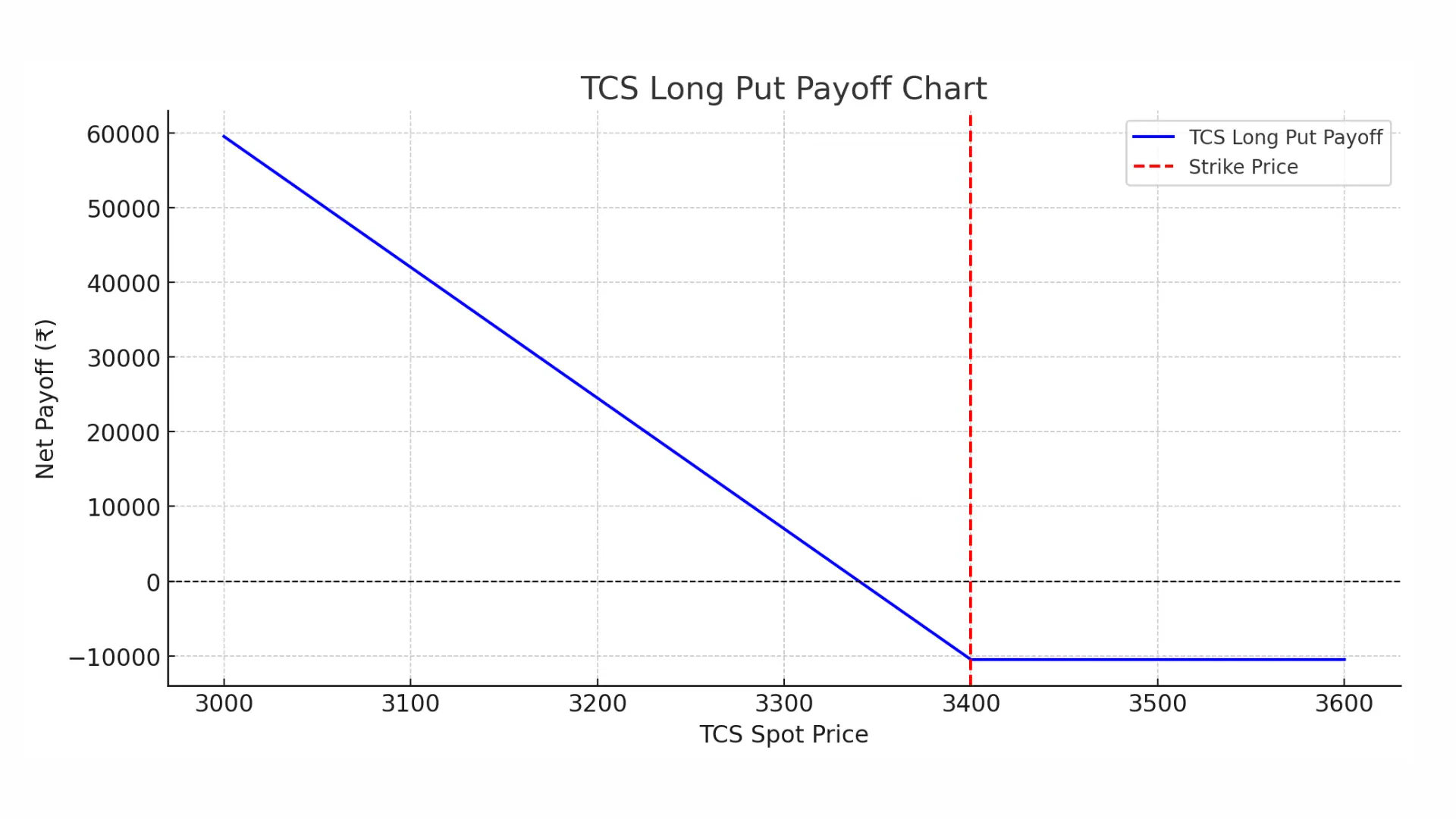
📌Example 1: TCS Stock
• Spot Price: TCS ₹3400
• Put Option Strike Price: ₹3400
• Premium: ₹60
• Lot Size: 175 shares
• Total Cost (Premium): ₹10500
Scenario A: Stock stays at ₹3400
• Option expires worthless.
• Loss = ₹10500 (maximum possible loss)
Scenario B: Stock rises to ₹3500
• Option again expires worthless.
• Loss = ₹10500
Scenario C: Stock falls to ₹3200
• Intrinsic Value = ₹200 × 175= ₹35,000
• Profit = ₹35,000 - ₹10500= ₹24,500
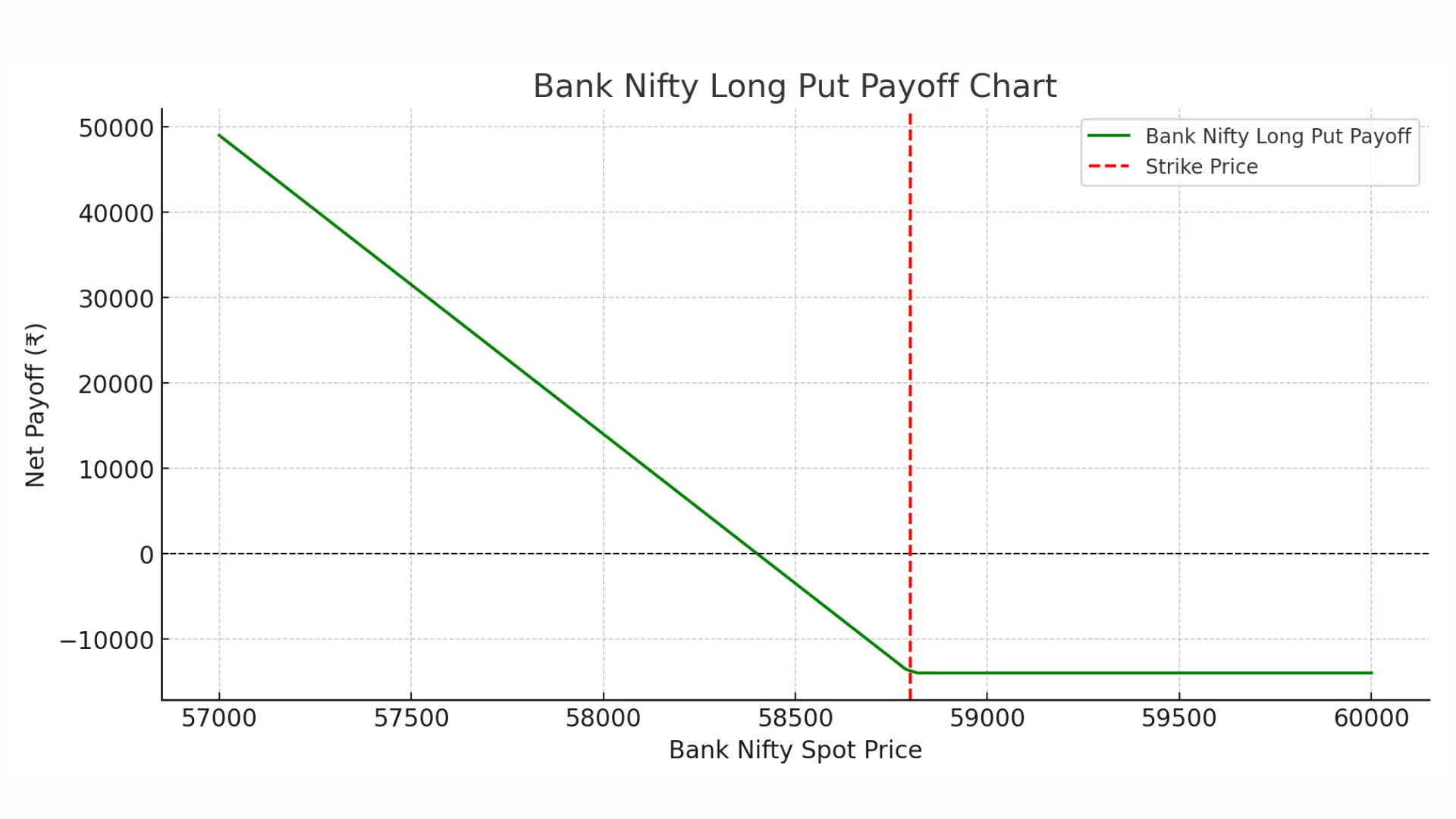
📌Example 2: Bank Nifty
- Bank Nifty Spot Price: ₹58,900
- Strike Price: ₹58,800
- Premium Paid: ₹400
- Lot Size: 35
- Total Cost: ₹14,000
- Breakeven Price: ₹58,400
| Expiry Price | Payoff (₹) | Net Profit (₹) |
| 58,000 | 28,000 | 14,000 |
| 58,200 | 21,000 | 7,000 |
| 58,400 | 14,000 | 0 |
| 58,600 | 7,000 | -7,000 |
| 58,800 | 0 | -14,000 (Max loss) |
| 59,000 | 0 | -14,000 |
📉Risk & Reward Profile
- Maximum Loss = Premium Paid
- Maximum Profit = Theoretically Unlimited (if underlying price falls to zero)
- Breakeven Point = Strike Price – Premium Paid
✅Pros and ❌Cons
✅ Pros:
- Limited, predefined risk
- High profit potential in falling markets
- No margin requirement
- Simple to execute
❌ Cons:
- 100% premium loss if the asset doesn’t move below the strike price
- Time decay works against the position
🏁How to Exit a Long Put
- Sell the Put Option before expiry to book profits or minimize losses
- Hold till expiry if expecting a strong downside
- Avoid letting OTM (out-of-the-money) puts expire worthless unnecessarily
📌Final Thoughts
The Long Put strategy is an excellent choice for traders expecting a downward move in an underlying stock or index. It's especially useful when you want to take a bearish bet while keeping your risk low and defined.
Whether you're a beginner or an experienced trader, this simple yet effective strategy can be a valuable tool in your options trading playbook.

