Table of Contents
- What Is a Long Call Option Strategy?
- When Should You Use a Long Call Strategy?
- How Does It Work?
- Real-World Example 1: Bank Nifty
- Real-World Example 2: NIFTY
- How to Exit a Long Call Trade?
- Benefits of Long Call Strategy
- Limitations of Long Call Strategy
- Profit & Loss Summary
- Strategy Summary
- Final Thoughts
What Is a Long Call Option Strategy?
A Long Call is a basic options trading strategy used when a trader expects the price of a stock or index to rise. This strategy involves buying a single call option, giving the trader the right (but not the obligation) to purchase the underlying asset at a specific price (called the strike price) before the expiry date.
The risk is limited to the premium paid for the option, while the profit potential is unlimited, making it a popular strategy among beginner and intermediate traders.
Risk: Limited to the premium paid. Reward: Unlimited.
When Should You Use a Long Call Strategy?
This strategy is ideal when you are bullish on the market or a specific stock. If you believe a stock (like Reliance, TCS, or Nifty Index) will increase in value in the short term, buying a call option can be a cost-effective way to benefit from the upside without purchasing the actual stock.
How Does It Work?
Pay a premium to buy a call option. If the stock rises above the breakeven (Strike + Premium), you profit. If it stays below strike, you lose only the premium.
- ✅ Maximum Loss: Limited to the premium paid
- ✅ Maximum Profit: Unlimited
- ✅ Breakeven Point: Strike Price + Premium
Real-World Example 1: Bank Nifty
Trade Setup:
- Current Spot: ₹56,900
- Strike Price: ₹56,800
- Premium: ₹800
- Lot Size: 35
- Breakeven Point: ₹56,800 + ₹800= ₹57,600
| Bank Nifty on Expiry (₹) | Premium Payoff (₹) | Exercise Payoff (₹) | Net Payoff (₹) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 56,800 | -28,000 | 0 | -28,000 |
| 57,000 | -28,000 | 7,000 | -21,000 |
| 57,200 | -28,000 | 14,000 | -14,000 |
| 57,400 | -28,000 | 21,000 | +7,000 |
| 57,600 | -28,000 | 28,000 | 0 |
| 57,800 | -28,000 | 35,000 | +7,000 |
| 58,000 | -28,000 | 42,000 | +14,000 |
Here's the payoff graph for the Bank Nifty Long Call strategy:
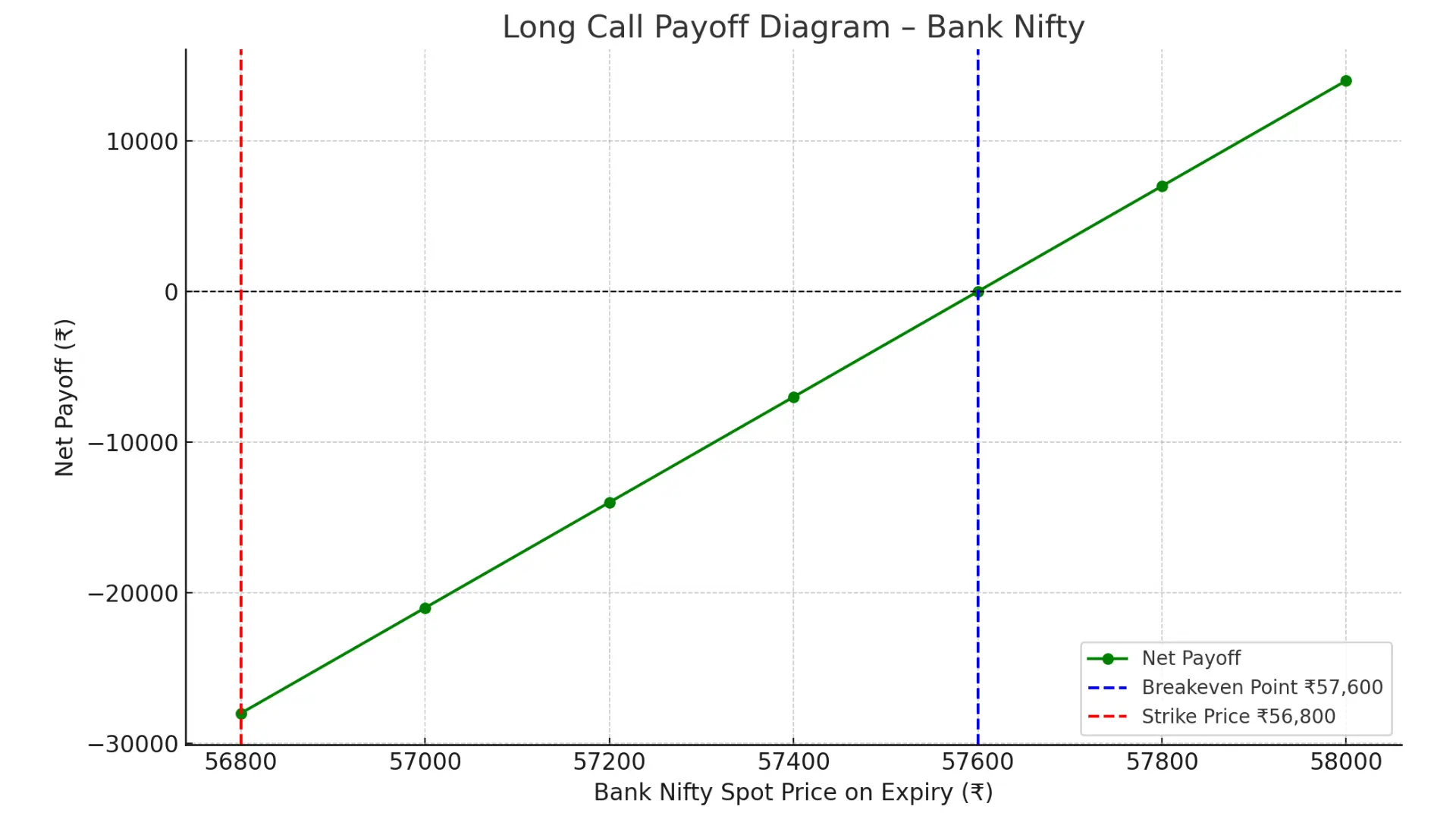
- 📍 Red Line = Strike Price (₹56,800)
- 📍 Blue Line = Breakeven Point (₹57,600)
- ✅ Green Line = Net Payoff Curve
This clearly shows:
- Loss is capped at ₹28,000 (premium paid)
- Profit rises as the price moves above ₹57,600
Let me know if you want this as an image file or want to create another one for NIFTY!
Real-World Example 2: NIFTY
- Nifty Spot: ₹25,550
- Strike Price: ₹25,750
- Premium: ₹40
- Lot Size: 75
- Total Premium Cost: ₹3,000
- Breakeven: ₹25,790(25,750+40)
| Nifty on Expiry (₹) | Net Payoff (₹) |
|---|---|
| 25,200 | -3,000 |
| 25,500 | -3,000 |
| 25,790 | 0 |
| 25,800 | +750 |
| 25,900 | +8,250 |
| 26,000 | +15,750 |
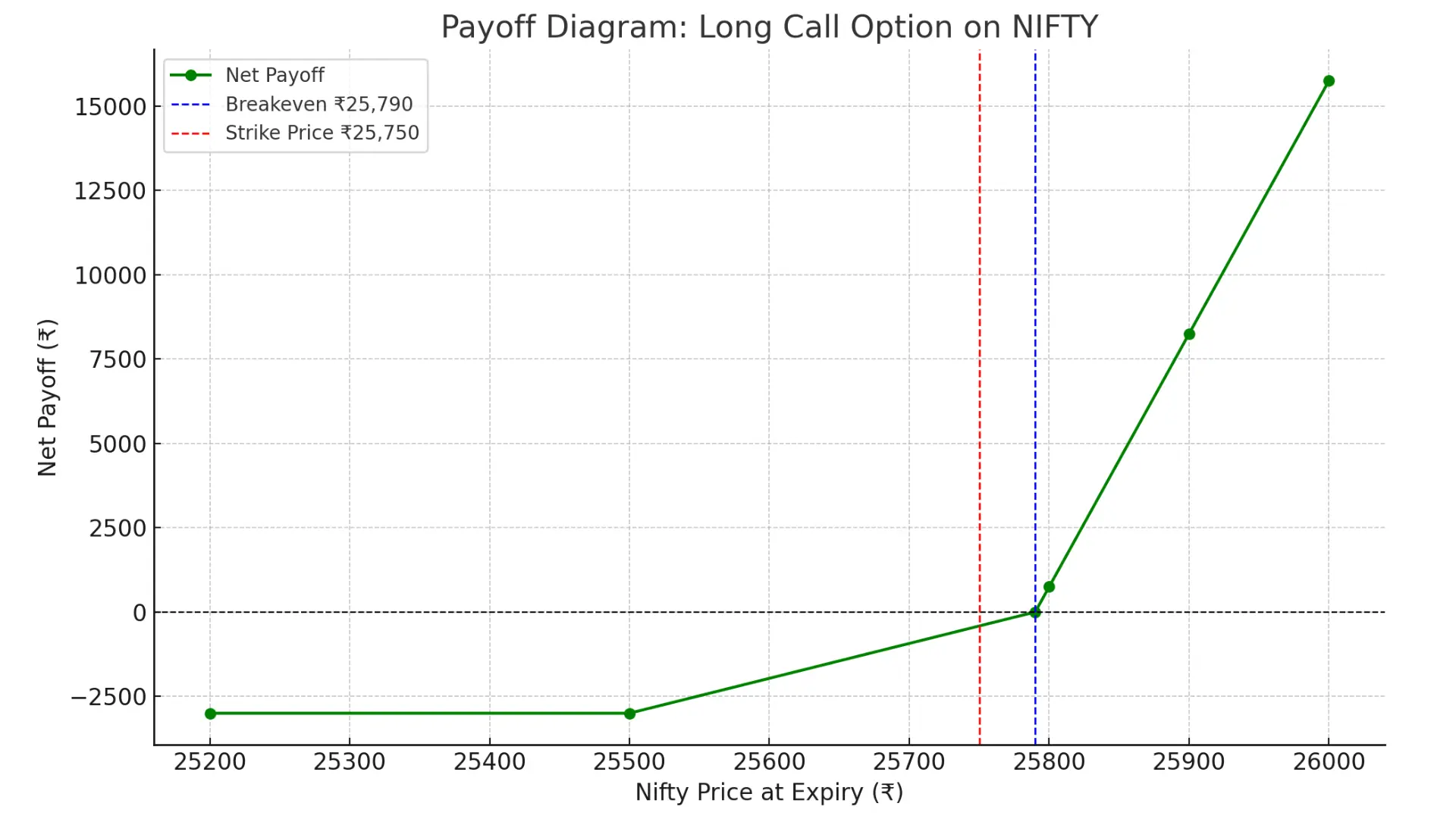
Here's the payoff diagram for the NIFTY Long Call Option strategy:
- The strike price is marked at ₹25,750 (red dashed line).
- The breakeven point is ₹25,790 (blue dashed line).
- The curve shows your net profit or loss based on Nifty’s expiry price.
How to Exit a Long Call Trade?
- Sell the Call Option before expiry if it's in profit.
- Let the Option Expire and exercise it if it's in the money.
Benefits of Long Call Strategy
- 🔒 Limited Risk: Loss is capped at the premium paid.
- 💰 High Reward: Unlimited profit potential on upside.
- 💸 Capital Efficient: Cheaper than buying the underlying stock.
Limitations of Long Call Strategy
- ⏳ Time Decay: Options lose value with time.
- 💸 Premium Loss: Entire premium is lost if price doesn’t rise.
Profit & Loss Summary
| Scenario | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Underlying closes above breakeven | Profit (Unlimited) |
| Underlying closes below strike | Loss = Premium Paid |
Strategy Summary
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| 📈 Market View | Bullish |
| 🔐 Risk | Limited to premium paid |
| 💰 Reward | Unlimited |
| 🎯 Breakeven | Strike Price + Premium |
| 🏁 Max Profit | When price rises well above strike |
| ⚠️ Max Loss | Premium paid only |
Final Thoughts
The Long Call Option strategy is a powerful yet simple way to profit from a bullish view while capping losses. It's a great entry-level strategy during earnings or high-volatility events.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a Long Call option strategy?
A: It is a bullish options trading strategy where a trader buys a call option, limiting loss to the premium paid and gaining from price rises.
Q: When should I use a Long Call?
A: When you're bullish on a stock or index and expect its price to rise before the option's expiry.
Q: What is the risk in a Long Call strategy?
A: The maximum risk is limited to the premium you pay to buy the call option.

