Table of Contents
- What is IPO Listing?
- IPO Listing Date
- IPO Listing Process in India
- IPO Listing Time
- IPO Listing Price
- IPO Circuit Limits on Listing Day
- IPO Shares Listing Groups (NSE & BSE)
- IPO Listing Price vs Issue Price vs Current Price
- Conclusion
📝What is IPO Listing?
An IPO listing is the process through which a company’s shares, initially offered during its Initial Public Offering (IPO), are listed on a stock exchange, making them available for public trading. Once listed, these shares become accessible to every investor through stock brokers, opening the gateway to the secondary market.
This article offers a detailed explanation of the IPO listing process in India. From listing dates and timings to price discovery and exchange-specific groupings, we’ve covered every angle to help you understand this important event in a company’s public journey.
📅 What is the IPO Listing Date?
The IPO listing date refers to the first day when a company’s shares are officially admitted for trading on a stock exchange like the NSE (National Stock Exchange) or the BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange).
This date typically occurs three working days after the closure of the IPO subscription window, following the latest SEBI guidelines effective from December 1, 2023. Investors can find the listing date on stock exchange websites.
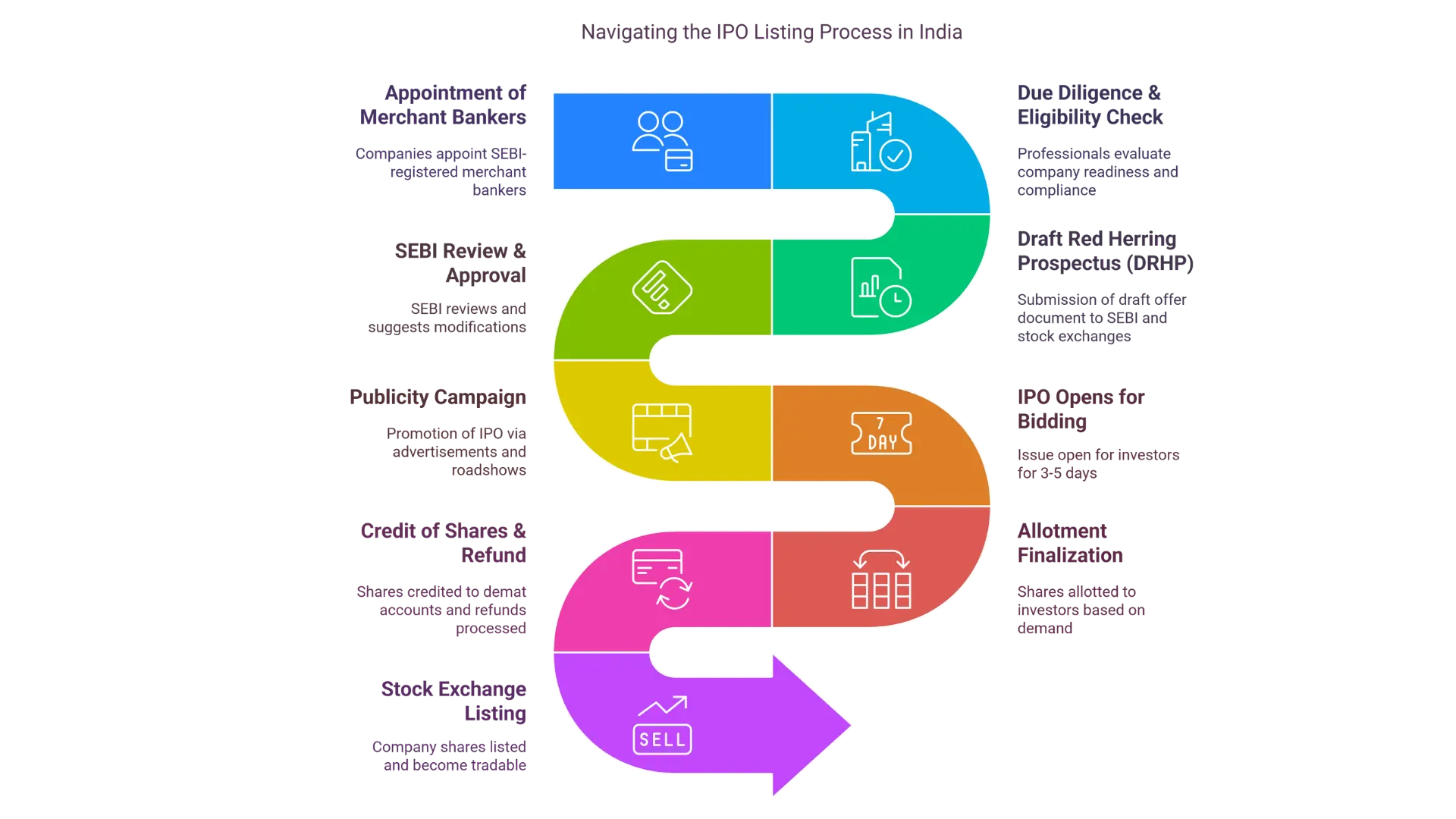
📈 IPO Listing Process in India: Step-by-Step
The process of listing a company’s shares on the stock exchange involves multiple crucial steps. Here's a step-by-step breakdown of the IPO listing process in India:
- Appointment of Merchant Bankers: Companies appoint SEBI-registered merchant bankers (also known as lead managers).
- Due Diligence & Eligibility Check: These professionals evaluate the company’s readiness and compliance for IPO listing.
- Draft Red Herring Prospectus (DRHP): Merchant bankers submit the draft offer document to SEBI and the stock exchanges.
- SEBI Review & Approval: SEBI reviews and suggests any modifications before giving the go-ahead.
- Publicity Campaign: The company promotes the IPO via advertisements, roadshows, and public relations.
- IPO Opens for Bidding: The issue is open for investors for 3-5 days.
- Allotment Finalization: Shares are allotted to investors based on subscription demand.
- Credit of Shares & Refund: Shares are credited to investors’ demat accounts, and refunds are processed.
- Stock Exchange Listing: Finally, the company’s shares are listed on the chosen stock exchange(s) and become tradable.
🕘 IPO Listing Time: When Does Trading Begin?
The IPO listing day begins with a pre-open session, typically starting at 9:00 AM, followed by regular market hours. Here’s a breakdown of how the day unfolds:
✅ Pre-Open Trading Session (9:00 AM - 10:00 AM)
This session is conducted exclusively on the listing day to determine the listing price based on demand and supply.
| Time | Activity |
|---|---|
| 9:00 AM – 9:45 AM | Order placement, modification, and cancellation |
| 9:45 AM – 9:55 AM | Order matching and price discovery (equilibrium price) |
| 9:55 AM – 10:00 AM | Buffer time before regular trading begins |
💡 Only limit orders are accepted during the pre-open session. Market orders are not permitted.
🔄 Regular Trading Session (Starts at 10:00 AM)
After the pre-open session concludes, the IPO stock begins trading in the normal market window just like any other stock.
💵 What is IPO Listing Price?
The IPO listing price is the price at which the stock gets listed on the stock exchange. It’s determined during the pre-open session through a process called equilibrium pricing, where investor demand meets supply.
💡 Example of Equilibrium Pricing:
- BSE demand: ₹120 for 300 shares
- NSE demand: ₹100 for 500 shares
| Listing Price (Common Equilibrium Price) =(₹120×300 + ₹100×500) / 800 = ₹107.50 |
The stock’s price band on the listing day is set at ±5% of this price.
📊 IPO Listing Day Circuit Limits
To maintain market stability, stock exchanges impose circuit limits on IPO stocks. These limits are calculated as a percentage of the IPO listing price:
| IPO Size | Circuit Limit |
|---|---|
| Up to ₹250 crores | ±5% |
| Above ₹250 crores | ±20% |
These caps prevent extreme price volatility on the day of listing.
🏷️ IPO Shares Listing Groups Explained
After an IPO, the stock is categorized into different listing groups by exchanges like BSE and NSE, based on issue size and market capitalization.
🔹 BSE Listing Groups
| Group Code | Criteria | Settlement | Intraday Trading |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Market Cap ≥ ₹1 lakh crore | Rolling | Yes |
| B | Issue Size > ₹250 crores | Rolling | Yes |
| T | Issue Size ≤ ₹250 crores | Trade-to-Trade | No |
🔸 NSE Series Codes
| Series | Criteria | Settlement | Intraday Allowed |
|---|---|---|---|
| EQ | Issue Size > ₹250 crores | Rolling | Yes |
| BE | Issue Size ≤ ₹250 crores | Trade-to-Trade | No |
🏢 InvITs and REITs Group Codes
| Security | Series/Group | Settlement Type | Exchange |
|---|---|---|---|
| InvITs | IV / ID | Rolling / TFT | NSE |
| REITs | RR / RT | Rolling / TFT | NSE |
📌 Note: IPOs with issue size up to ₹250 crores are mandatorily traded in the Trade-for-Trade (TFT) segment for the first 10 days after listing.

🔁 Comparison: IPO Listing Price vs. Issue Price vs. Market Price
Let’s understand the key differences between various pricing terms associated with an IPO:
1️⃣ IPO Listing Price vs. Current Price
| IPO Listing Price | Current Market Price |
|---|---|
| Set during pre-open session | Changes continuously in the market |
| Announced at 9:55 AM on listing day | Fluctuates throughout the day |
2️⃣ Issue Price vs. Listing Price
| Issue Price | Listing Price |
|---|---|
| Price offered during IPO | Opening price on listing day |
| Decided by the company & bankers | Determined by market demand |
3️⃣ Listing Price = Opening Price?
Yes, the listing price is effectively the opening price on the day of listing, derived from pre-open session demand-supply dynamics.
📌 How to Trade IPO Shares on Listing Day?
Want to buy or sell IPO shares as soon as they list? Here’s what you need to do:
Steps for Pre-Open Orders:
- Place a limit order before 9:45 AM on the listing day.
- If your price matches or is favorable, your order will be executed during the pre-open window.
- Unexecuted orders move to the regular session.
Example:
| Order Type | Limit Price | Listing Price = ₹510 | Executed? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buy | ₹505 | No | ❌ |
| Buy | ₹510 | Yes | ✅ |
| Sell | ₹505 | Yes | ✅ |
✅ Key Takeaways
- IPO listing allows public trading of a company’s shares.
- Pre-open session plays a vital role in price discovery.
- Circuit limits and group codes regulate trading to ensure fairness.
- Investors can participate in the listing day through limit orders.
🏁 Conclusion
The IPO listing marks a critical transition for any company moving from private to public ownership. Understanding how listing dates, prices, timings, and stock exchange protocols work empowers investors to make smart, timely decisions.
Whether you’re a new investor or a seasoned trader, knowing the ins and outs of IPO listings in India is essential to maximize opportunities and manage risk in the stock market. With the right knowledge and strategy, IPO investing can be a powerful tool in building wealth over time.

