Table of Contents
IPO Guidelines for Mainboard and SME Listings in India
This chapter outlines the eligibility norms and requirements for companies seeking to launch Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) on both the Mainboard and SME platforms. It also covers pre-IPO conditions set by regulatory authorities such as SEBI, NSE, and BSE.
1. Mainboard IPO Norms and Eligibility
Mainboard IPOs are meant for well-established companies with a minimum paid-up capital of ₹10 crore. These IPOs are listed on major stock exchanges like the NSE and BSE and are governed by the SEBI (Issue of Capital and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2018.
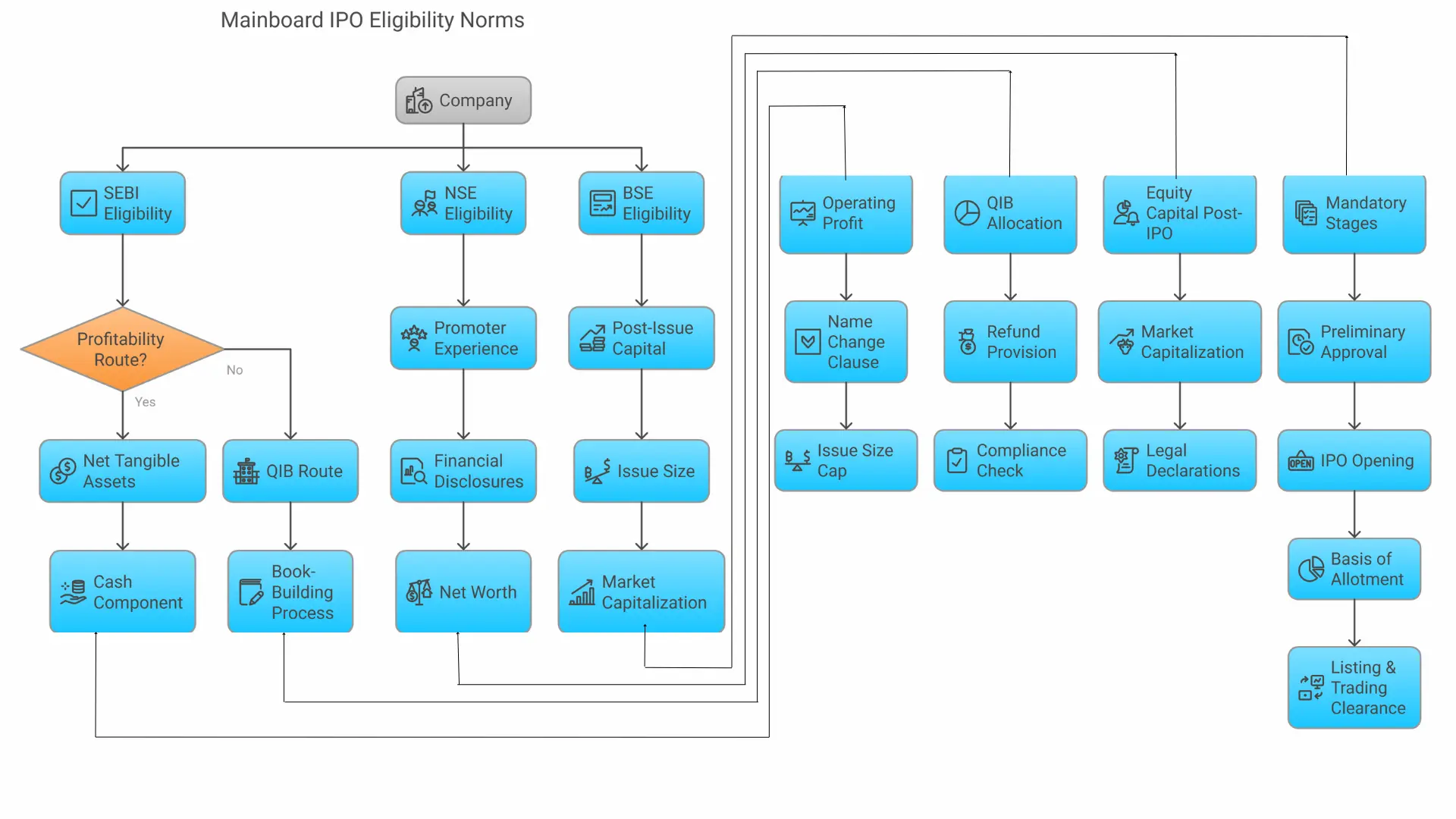
A. SEBI's Mainboard IPO Eligibility Norms
SEBI has laid down two primary pathways for companies to meet IPO eligibility standards:
i. Profitability Route (Entry Norm I)
To qualify under this route, companies must fulfill all the conditions listed below:
- Net Tangible Assets: At least ₹3 crore in each of the preceding three financial years.
- Cash Component: No more than 50% of the tangible assets should be in cash or cash equivalents.
- Operating Profit: Minimum average pre-tax profit of ₹15 crore during any three of the last five years.
- Name Change Clause: If the company changed its name in the past year, at least 50% of its last year’s revenue must have come from the renamed business activity.
- Issue Size Cap: The IPO size should not exceed five times the pre-issue net worth of the company.
ii. QIB Route (Entry Norm II)
Designed for promising companies unable to meet profitability norms, this route includes:
- Book-Building Process: IPO must be issued via this mechanism.
- QIB Allocation: At least 75% of the offering must be reserved for Qualified Institutional Buyers.
- Refund Provision: Subscription amount must be refunded if QIB quota is under-subscribed.
- Compliance Check: No promoters, directors, or stakeholders should have a history of legal or regulatory restrictions in capital markets.
B. NSE IPO Eligibility Norms
In addition to SEBI norms, companies aiming to list on the NSE Mainboard must meet these conditions:
- Promoter Experience: At least one promoter should have 3+ years of industry-specific experience.
- Financial Disclosures: Annual reports for the last three financial years must be submitted.
- Net Worth: Must be positive (required only if issue size is below ₹500 crore).
- Equity Capital Post-IPO: Should exceed ₹10 crore.
- Market Capitalization: Must be greater than ₹25 crore.
- Legal Declarations: The company must not be involved in insolvency, winding-up, or similar proceedings.
C. BSE IPO Eligibility Norms
Eligibility norms for BSE listings are closely aligned with those of NSE:
- Post-Issue Capital: Minimum ₹10 crore.
- Issue Size: At least ₹10 crore.
- Market Capitalization: Should be ₹25 crore or more.
- Mandatory Stages:
- Preliminary Approval
- IPO Opening
- Basis of Allotment
- Listing & Trading Clearance
Additional requirements include obtaining prior permission from BSE for brand usage in official documents, ensuring shares are fully dematerialized, and depositing 1% of the issue value with the designated exchange.
2. SME IPO Guidelines and Requirements
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) often lack the historical financial depth required for Mainboard IPOs. To support them, NSE and BSE have created dedicated platforms — NSE Emerge and BSE SME — allowing these companies to access public capital more easily.
The post-issue paid-up capital for SMEs must not exceed ₹25 crore. While SEBI relaxes some requirements for SMEs, directors and promoters must still meet stringent compliance standards, similar to those for regular IPOs.
A. BSE SME IPO Eligibility Criteria
Companies planning to go public through the BSE SME platform must adhere to the following:
| Parameter | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Net Worth | Minimum ₹1 crore for the past two financial years |
| Net Tangible Assets | At least ₹3 crore in the preceding financial year |
| Business Track Record | Operational history of at least 3 years |
| Operating Profits | Positive in 2 of the last 3 years (mandatory in the latest year) |
| Leverage Ratio | Not more than 3:1 |
Other prerequisites include:
- No regulatory bans or suspensions involving promoters.
- Directors must not be involved with delisted or blacklisted entities.
- A functional company website is mandatory.
- Company must be registered with both NSDL and CDSL.
- Shares must be tradeable in demat form.
- Promoter list should remain unchanged for a year prior to listing.
- No current involvement in BIFR or insolvency proceedings.
Additional Criteria for Specialized Companies
Broking Companies:
- Net worth ₹5 crore in 2 of 3 years OR ₹25 crore in 3 of 5 years.
- Net Tangible Assets: ₹3 crore.
- Post-issue paid-up capital: ₹3 crore.
Microfinance Companies:
- Assets Under Management: ₹100 crore+
- Client Base: 10,000+
- No public deposits accepted
B. NSE SME IPO (NSE Emerge) Eligibility Criteria
For listing on NSE Emerge, the company must satisfy the following:
- Registered under Companies Act, 1956 or 2013.
- Minimum three years of operational history.
- At least one promoter must have 3+ years of industry experience.
- Promoters must hold 20% equity post-IPO, individually or collectively.
- Must show operating profit and positive net worth in at least 2 out of the last 3 years.
- No ongoing insolvency or winding-up proceedings.
- No serious regulatory or disciplinary actions in the last 3 years.
Conclusion
Both Mainboard and SME IPOs come with their own set of challenges and benefits. While Mainboard IPOs demand strong financials, SME IPOs provide growing enterprises with easier access to capital markets. Adherence to compliance and eligibility ensures investor confidence and sustainable business expansion.

