📌 Table of Contents
🧠 Introduction
The Bear Call Spread—also known as the Bear Call Credit Spread—is an options trading strategy designed for bearish or range-bound market conditions. This strategy involves selling an in-the-money (ITM) call option and buying an out-of-the-money (OTM) call option with the same underlying asset and expiry date. It’s a low-risk, limited-reward strategy ideal for traders who expect a moderate decline or stability in the market.
📌 Key Highlights
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Strategy Type | Bearish (Credit Spread) |
| Instruments Traded | Call Options |
| Positions Involved | 2 (1 Short Call, 1 Long Call) |
| Risk Profile | Limited |
| Reward Profile | Limited |
| Breakeven Point | Strike Price of Short Call + Net Premium |
🛠 How the Bear Call Spread Strategy Works
The Bear Call Spread is implemented as follows:
- Sell a Call Option with a lower strike price (ITM)
- Buy a Call Option with a higher strike price (OTM)
💰 Net Credit = Premium Received – Premium Paid
You earn a net credit at the time of initiating the trade. The goal is for both options to expire worthless, allowing you to keep the net premium as profit.
📊 Bear Call Spread Example – NIFTY
Assume NIFTY Spot Price = ₹25,400
| Order Type | Strike Price |
|---|---|
| Buy 1 OTM Call | NIFTY 25600 CE |
| Sell 1 ITM Call | NIFTY 25200 CE |
If NIFTY stays below 25,200, both options expire worthless. You retain the net premium as your maximum profit.
🧾 Bear Call Spread Example – Stock Options
Stock Spot Price = TCS ₹3330
| Option Type | Strike Price | Premium (₹) | Lot Size |
| Buy July 3400 Call | ₹3400 | ₹20 | 175 shares |
| Sell July 3300 Call | ₹3300 | ₹60 | 175 shares |
- Total Premium Paid = ₹3500
- Total Premium Received = ₹10500
- Net Credit = ₹7000
✅ Scenario 1: Stock remains at ₹3330
Both options expire worthless.
Profit = ₹7000 (Maximum Profit)
❌ Scenario 2: Stock rises to ₹3450
- Loss on Short Call = ₹26250
- Gain on Long Call = ₹8750
- Net Loss = ₹17500(Maximum Loss)
✅ Scenario 3: Stock drops to ₹3250
Both options expire worthless.
Profit = ₹7000 (Maximum Profit)
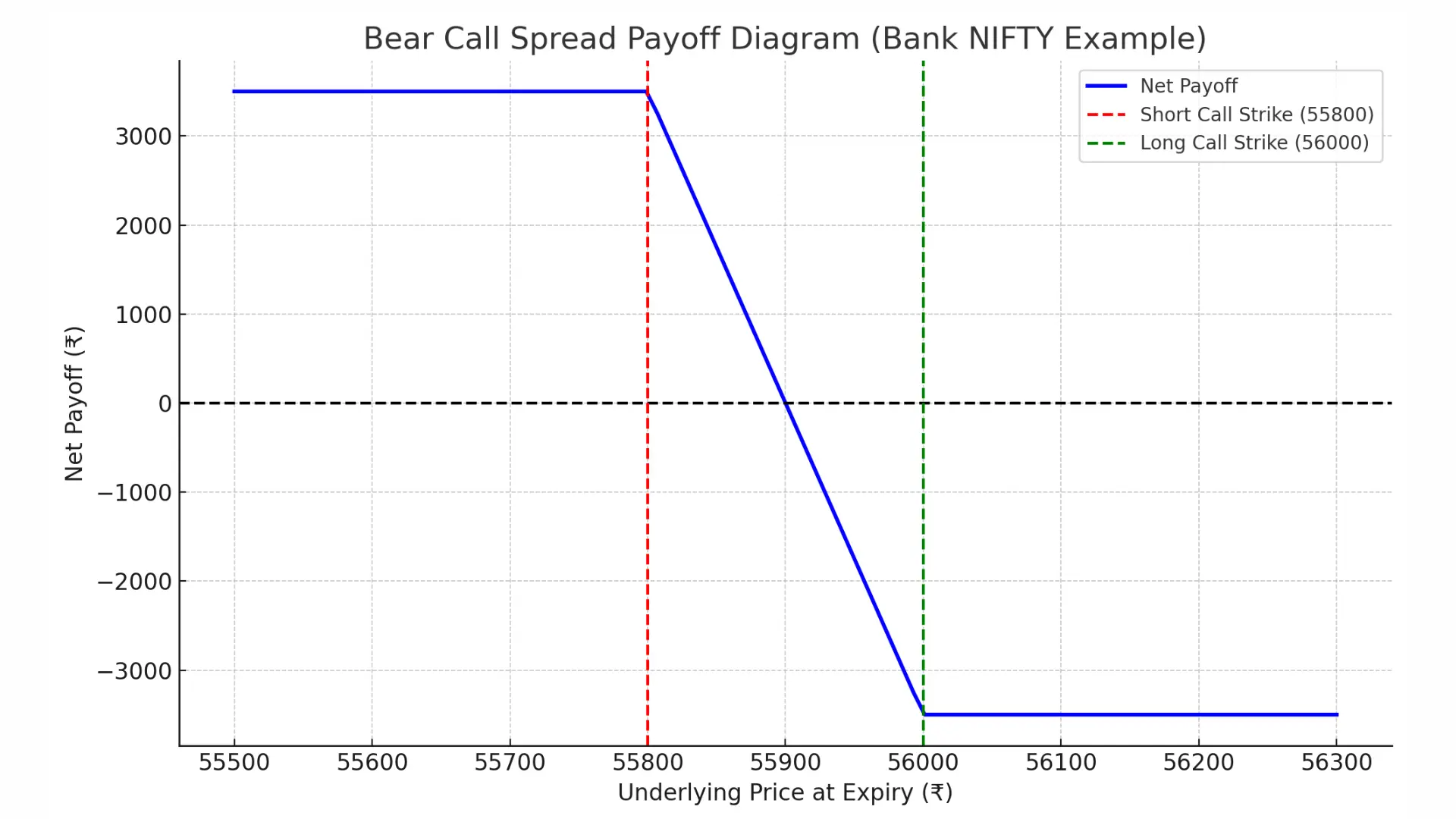
🏦 Bear Call Spread Example – Bank NIFTY
| Details | Values |
|---|---|
| Spot Price | ₹55,900 |
| Lot Size | 35 |
| Buy OTM Call (56000 CE) | ₹400 (₹14,000 total) |
| Sell ITM Call (55800 CE) | ₹500 (₹17,500 total) |
| Net Premium | ₹100 (₹3,500 total) |
| Breakeven Point | ₹55,900 |
| Max Profit | ₹3,500 |
| Max Loss | ₹3,500 |
📈 Payoff Table
| Expiry Price | Profit/Loss (₹) |
|---|---|
| 55500 | +3,500 |
| 55700 | +3,500 |
| 55900 | 0 (Breakeven) |
| 56100 | –3,500 |
| 56300 | –3,500 |
⚖️ Profit & Loss Overview
- Max Profit = Net Premium Received
- Max Loss = Difference in Strike Prices – Net Premium
- Breakeven = Short Call Strike + Net Premium
✅ Advantages of Bear Call Spread
- Profitable in flat or mildly bearish markets
- Lower margin requirement than naked calls
- Predefined risk and reward
- Easy to execute and manage
❌ Disadvantages of Bear Call Spread
- Limited profit potential
- Requires correct market direction
- Profitability depends on the price staying below the short call strike
🔄 How to Exit the Strategy?
- Let options expire worthless to retain the full premium
- Close position early by reversing both legs if the price reverses
📌 Best Use Case
When you're moderately bearish or expect range-bound movement in the underlying asset.
📋 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
❓ What is a Bear Call Spread strategy?
It's an options strategy where you sell an ITM call and buy an OTM call to earn a net credit.
❓ Is the Bear Call Spread strategy safe?
Yes, it's low-risk with defined loss and profit.
❓ What happens at expiry?
If the asset closes below the short call strike, both options expire worthless, and you keep the net premium.
❓ Can I exit early?
Yes, reverse the trade anytime before expiry.
❓ Which is better: Bear Call Spread or Naked Call?
Bear Call Spread is safer due to defined risk; naked calls have unlimited loss potential.

